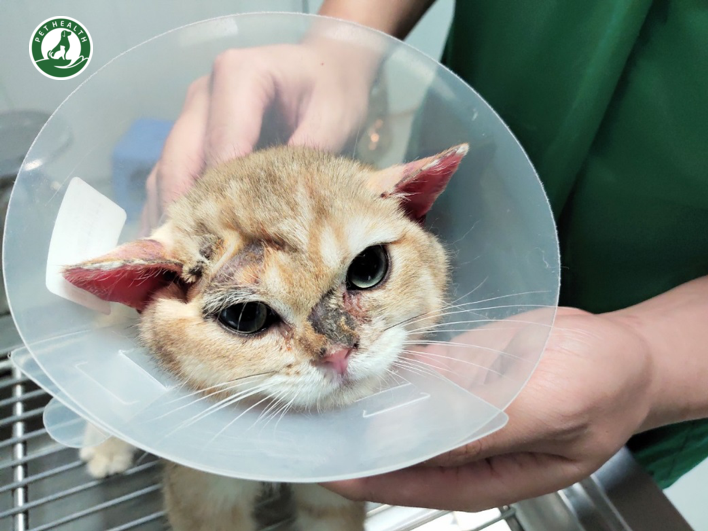
Beware of Fungal Skin Infections from Pet Dogs and Cats
Pet ownership brings joy, companionship, and numerous health benefits. However, it also comes with responsibilities, including ensuring your pet’s health and hygiene. One common yet often overlooked issue is fungal skin infections, which can spread from dogs and cats to humans. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of these infections is essential for every pet owner.
What Are Fungal Skin Infections?
Fungal skin infections in pets are caused by various fungal species, most commonly dermatophytes. The most prevalent type of dermatophytosis in pets is ringworm, despite its misleading name (it is not caused by a worm but by fungi of the genera Microsporum and Trichophyton). These infections thrive in warm, moist environments and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected animal, contaminated objects, or the environment.
How Do Pets Contract Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections can affect both healthy and immunocompromised pets. They are commonly transmitted through:
- Direct Contact: Pets can contract fungal infections by touching infected animals or contaminated surfaces, such as bedding, furniture, or grooming tools.
- Poor Hygiene: Dirty living conditions, lack of regular bathing, and neglecting pet grooming contribute to fungal growth.
- Weakened Immune System: Kittens, puppies, elderly pets, or animals with underlying health conditions are more susceptible.
- Outdoor Exposure: Pets that roam outside have a higher risk of coming into contact with infected animals or fungal spores in soil.
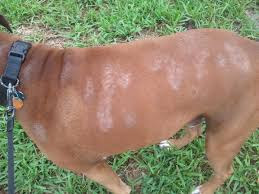
Symptoms of Fungal Infections in Dogs and Cats
Recognizing the symptoms of fungal infections early can prevent them from spreading. Common signs include:
- Circular bald patches with scaly or red skin
- Itchiness and excessive scratching
- Brittle or broken hairs
- Crusty or inflamed skin
- Dandruff or excessive shedding
- Infected nails, appearing discolored or thickened
If your pet shows any of these signs, it is crucial to seek veterinary care immediately to prevent further spread and complications.
How Can Fungal Infections Spread to Humans?
Fungal infections like ringworm are zoonotic, meaning they can transfer from animals to humans. People with compromised immune systems, young children, and the elderly are more vulnerable to infection. Transmission occurs through:
- Direct skin contact with an infected pet
- Contact with contaminated objects like pet bedding, brushes, and toys
- Scratches or bites from infected animals
In humans, ringworm appears as red, itchy, ring-shaped rashes on the skin, often on the hands, arms, or scalp. If you suspect infection, consult a doctor for appropriate antifungal treatment.
Prevention Tips for Pet Owners
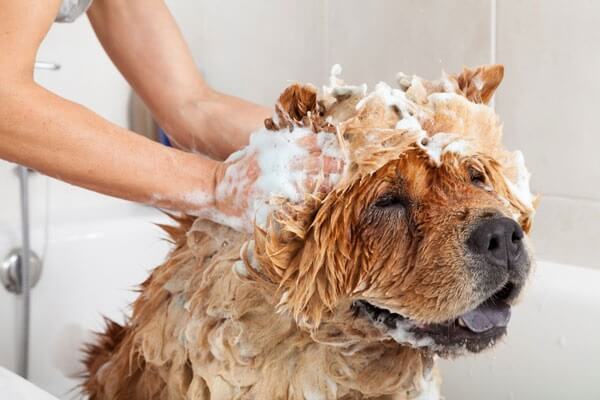

Preventing fungal infections requires a proactive approach to pet hygiene and environmental cleanliness. Here are some essential tips:
1. Regular Grooming and Hygiene
- Bathe pets regularly using antifungal shampoos if they are prone to infections.
- Brush their fur to remove dirt, debris, and possible fungal spores.
- Keep their nails trimmed to prevent fungal buildup.
2. Maintain a Clean Living Environment
- Wash pet bedding, blankets, and toys frequently.
- Disinfect grooming tools and litter boxes regularly.
- Vacuum and clean your home, especially areas where pets frequent.
3. Strengthen Your Pet’s Immune System
- Provide a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Ensure pets receive regular veterinary check-ups.
- Avoid exposure to infected animals or unsanitary environments.
4. Handle Pets with Care
- Wash hands thoroughly after touching pets, especially before eating.
- Wear gloves when treating an infected pet.
- Keep infected pets isolated from other animals and family members until fully recovered.
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections
If your pet contracts a fungal infection, timely treatment is necessary to prevent complications and transmission. Common treatments include:
1. Antifungal Medications
- Topical Treatments: Medicated shampoos, creams, or sprays containing miconazole or ketoconazole can help eliminate fungi.
- Oral Medications: Severe infections may require antifungal pills prescribed by a veterinarian.
2. Environmental Disinfection
- Clean and disinfect all surfaces that an infected pet has touched.
- Use antifungal sprays or wipes on pet accessories.
- Wash bedding and soft items in hot water with antifungal detergent.
3. Natural Remedies (Supportive Care)
- Coconut Oil: Has antifungal properties that can soothe irritated skin.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted in water, it can help as a topical treatment.
- Aloe Vera: Helps reduce inflammation and itching.
While natural remedies can provide relief, they should not replace veterinary-prescribed treatments.
Conclusion
Fungal skin infections in pets are a common but manageable issue. By maintaining good hygiene, providing proper care, and seeking timely treatment, pet owners can protect both their furry companions and themselves from infections. If you notice any signs of fungal infections in your pet, consult a veterinarian promptly. Awareness and preventive measures go a long way in ensuring the health and happiness of both pets and their human families
Read more: