Common Veterinary Vaccines and How to Choose the Right One
Why Veterinary Vaccination Matters
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to protect animals against dangerous infectious diseases. Whether you are a pet owner, a farmer, or a breeder, ensuring your animals are properly vaccinated not only safeguards their health but also helps prevent disease outbreaks in the community.
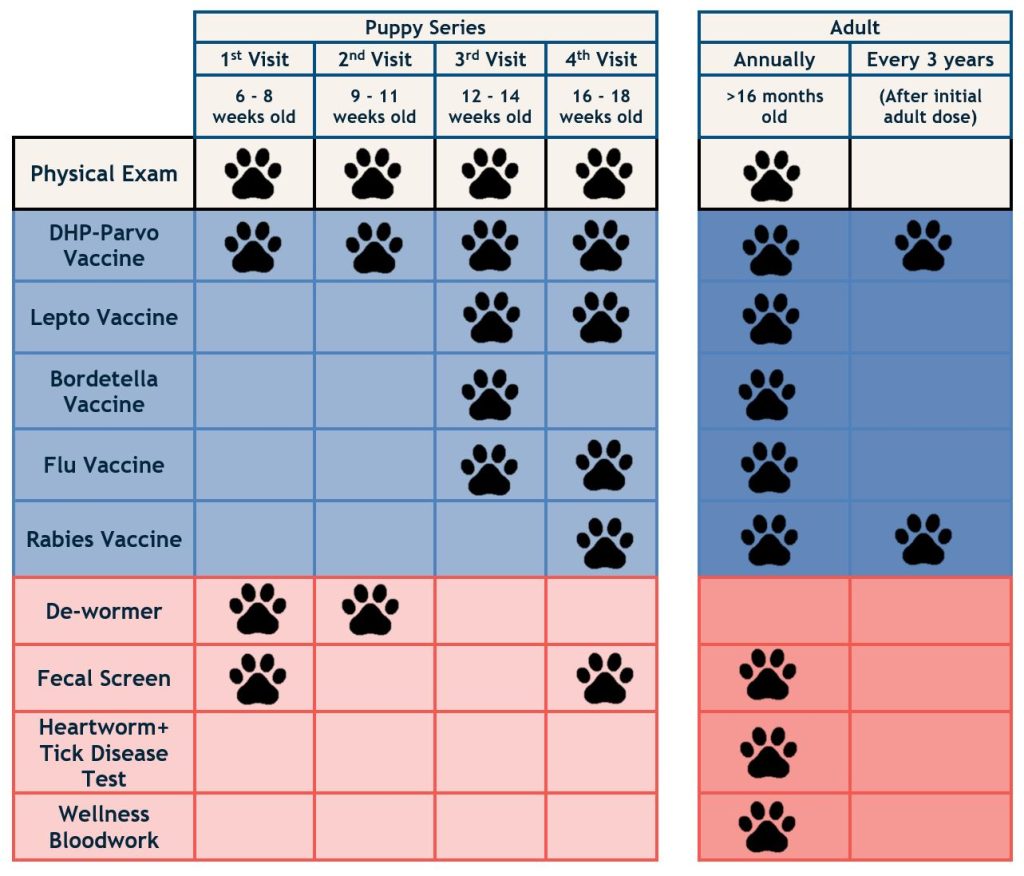
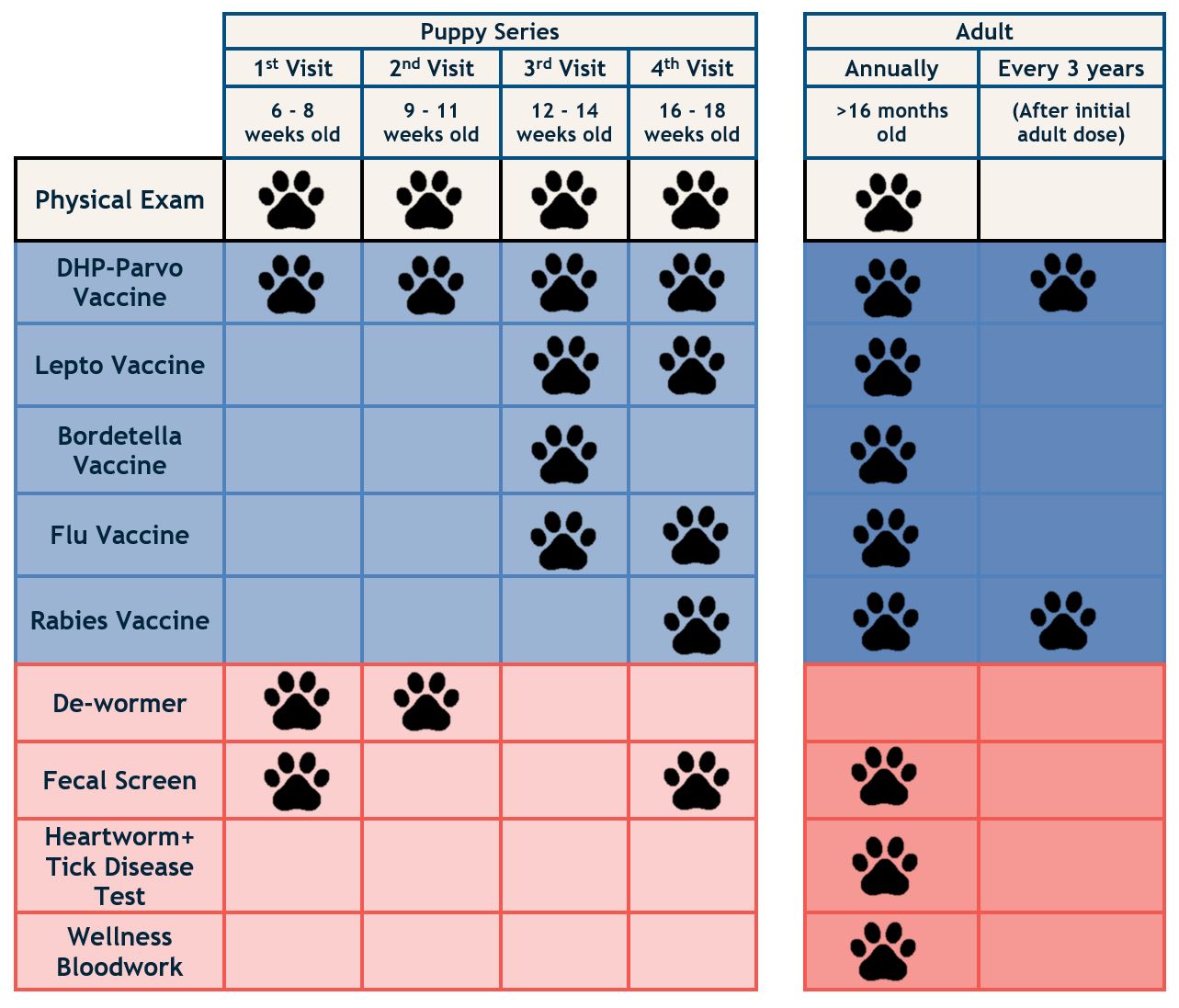
1. Common Veterinary Vaccines for Pets
🐶 Dogs
-
Rabies Vaccine: Protects against rabies, a deadly viral disease that can be transmitted to humans.
-
DHPP Vaccine: A combination vaccine against Distemper, Hepatitis (Adenovirus), Parvovirus, and Parainfluenza.
-
Leptospirosis Vaccine: Prevents leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can damage the kidneys and liver.
-
Bordetella (Kennel Cough) Vaccine: Recommended for dogs frequently in kennels, grooming salons, or parks.
🐱 Cats
-
Rabies Vaccine: Mandatory in many regions.
-
FVRCP Vaccine: Protects against Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis, Calicivirus, and Panleukopenia.
-
FeLV Vaccine: Shields cats from Feline Leukemia Virus, especially recommended for outdoor cats.
2. Common Veterinary Vaccines for Livestock
-
Cattle: Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD), Brucellosis, Blackleg, Anthrax.
-
Poultry: Newcastle Disease, Avian Influenza, Marek’s Disease, Infectious Bronchitis.
-
Pigs: Classical Swine Fever (CSF), Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), Erysipelas.
-
Sheep & Goats: Enterotoxemia, Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR), Bluetongue.
3. How to Choose the Right Vaccine
-
Consult a Veterinarian
Always seek professional advice before vaccination. The right vaccine depends on the animal’s age, breed, lifestyle, and local disease prevalence. -
Follow National Guidelines
Many countries have mandatory vaccination schedules (e.g., rabies for pets, FMD for livestock). Adhering to these is crucial for legal compliance and public safety. -
Assess Risk Factors
-
Indoor pets may need fewer vaccines compared to outdoor pets.
-
Farm animals in high-density settings often require broader protection.
-
-
Consider Combination Vaccines
Multivalent vaccines (e.g., DHPP for dogs, FVRCP for cats) reduce the number of injections and provide protection against multiple diseases at once. -
Regular Boosters Are Essential
Immunity decreases over time. Annual or multi-year booster shots are necessary to maintain effective protection.
4. Key Takeaways
-
Vaccines save lives and reduce the spread of infectious diseases.
-
The most common vaccines cover rabies, parvovirus, distemper, and respiratory diseases in pets, as well as foot-and-mouth, avian influenza, and swine fever in livestock.
-
Choosing the right vaccine should always be done with veterinary consultation.
xem thêm:
Dịch Vụ Vận Chuyển Thú Cưng Nội Địa Và Quốc Tế
Dịch Vụ Vận Chuyển Thú Cưng Từ Hà Nội Đi Sơn La Nhanh Chóng, An Toàn – Asia PATA